Periodontal Treatments – Supporting Gum Health and Oral Function
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a progressive inflammatory condition that begins with gingivitis, a mild form of gum inflammation. It is a leading cause of tooth loss among adults, making regular evaluation and timely management important.
While gum disease can cause red, swollen, tender, or bleeding gums, some individuals may not notice symptoms. Plaque bacteria can affect or irritate the soft tissues around the teeth, and without intervention, inflammation may progress, affecting gums and supporting structures. Over time, this can contribute to tooth mobility, shifting teeth, and potential tooth loss.
Diagnosis
A comprehensive periodontal examination is used to evaluate gum health and determine the severity of disease. Key measures include:
- Pocket Depth: The space between tooth and gum is measured; healthy pockets are typically 3 mm or less and do not bleed.
- Bleeding on Probing: Indicates inflammation and tissue response.
- Gingival Inflammation: Assesses redness, swelling, or tenderness of the gums.
- Tooth Mobility: Evaluates how securely teeth are anchored.
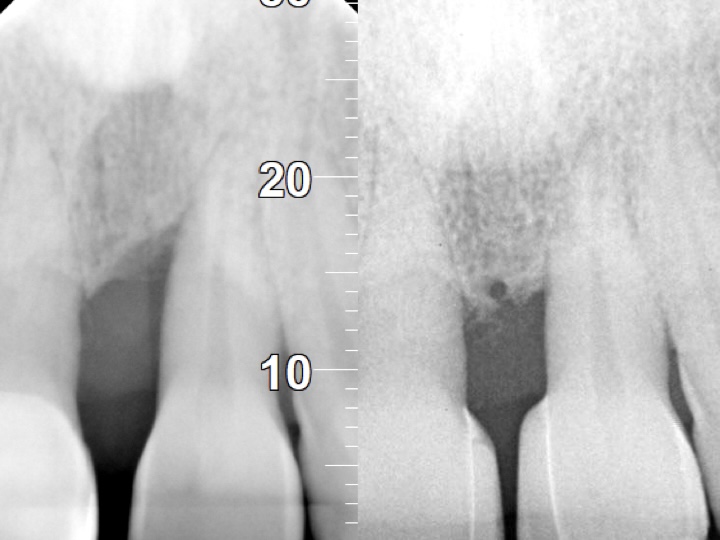
- Radiographic Bone Levels: X-rays assess supporting bone structure.
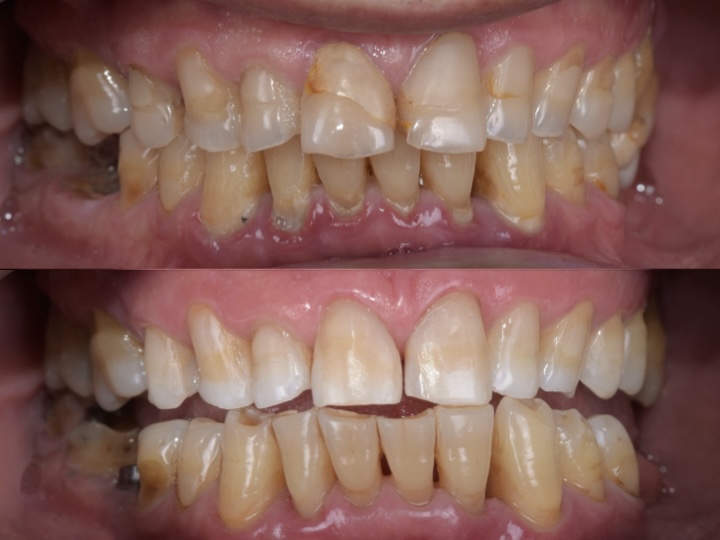
Stages of Periodontal Disease
- Gingivitis: The earliest, reversible stage; inflammation and bleeding occur without bone loss.
- Periodontitis: Plaque hardens into tartar, gum tissue recedes, pockets deepen, and mild to moderate bone loss may occur.
- Advanced Periodontitis: Progressive deterioration of gum, bone, and periodontal ligament; teeth may feel loose, with moderate to severe bone loss.
Treatment Approaches
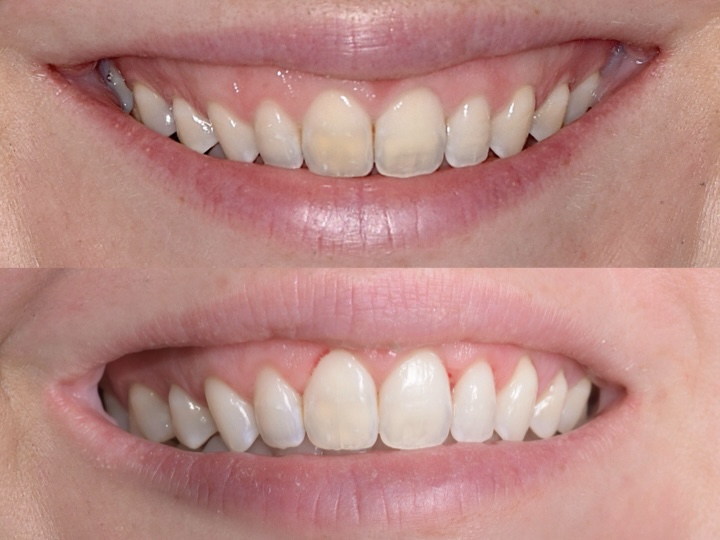
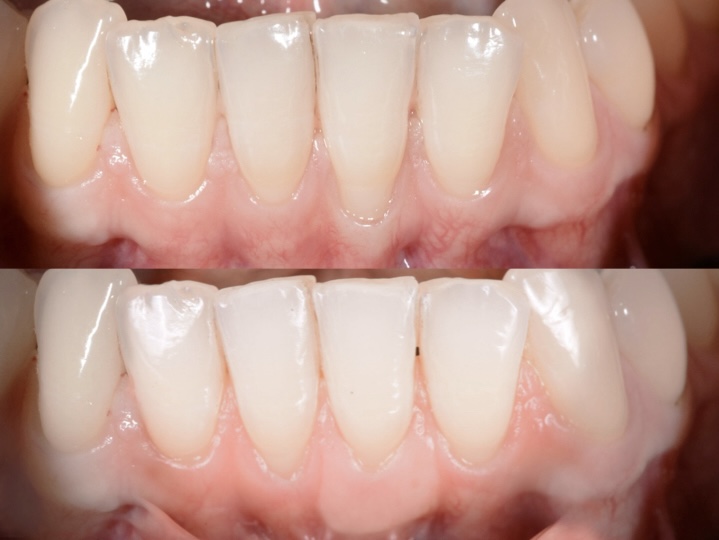
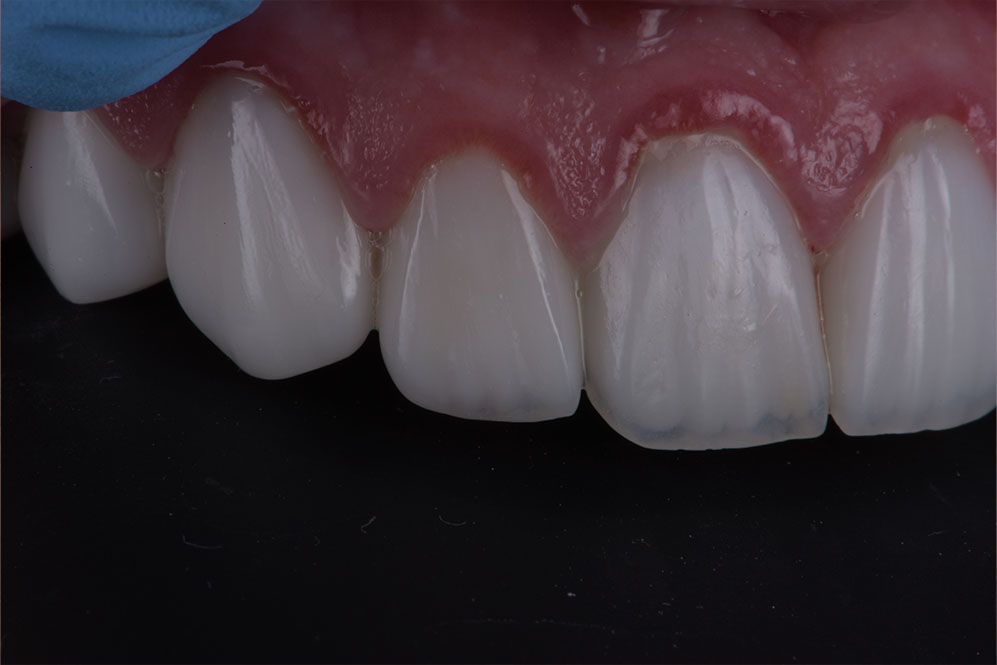
Periodontal treatments aim to halt disease progression, restore oral health, and support both function and appearance. Approaches may include:
-
Crown Lengthening: Adjusts gum tissue to improve tooth function or aesthetics.
-
Soft Tissue Grafts: Restore receded gums, protect exposed roots, and support gum coverage.
-
Scaling and Root Planing: Deep cleaning to remove plaque and tartar from teeth and roots, reducing inflammation.
-
Regenerative Procedures: Techniques to restore lost gum and bone tissue, supporting long-term periodontal health.
-
Other Targeted Periodontal Procedures: Reduce gum pockets, strengthen tissue attachment, and preserve affected teeth.
Importance of Timely Management
Periodontal disease is progressive. Early detection, personalized care, and routine maintenance are essential for maintaining gum health, preserving teeth, and supporting oral function.
Outcomes are individual and may vary according to each patient’s circumstances.
All images are the intellectual property of Dr. Catea and illustrate clinical work performed by him within the practice. Any reproduction, distribution, or use without prior written authorization is strictly prohibited.